Generative AI Delivers a Boost to Cloud Computing
Cloud computing companies are charting a recovery following a tough 18-month period characterized by challenging macro conditions and reductions in enterprise budgets. We are now witnessing a turning point driven by improving fundamentals, such as profitability.1 Another driver is the growing importance of generative AI. Spending on cloud computing is expected to increase by nearly 22% in 2023, and we expect that cloud software and infrastructure giants can capitalize on this trend by offering AI-incorporated solutions to customers.2 The growing use of AI-as-a-service is also an opportunity for cloud computing companies to incrementally monetize their offerings by upselling additional cloud infrastructure and services. We believe that these factors can potentially position companies in the cloud computing theme for better-than-expected revenue and profit growth as AI adoption picks pace.
Key Takeaways
- Cloud spending optimization brought by tightening economic conditions appears to be partly negated by enterprise investment in AI solutions.
- Hyperscalers and large cloud software players are embracing generative AI-based solutions to strengthen product portfolios and monetize incrementally.
- As enterprise adoption of generative AI grows, we expect consumption of ancillary cloud compute, storage, and other services to tick up and boost the Cloud Computing theme.
Earnings Show Cloud Spending Optimization May Be Nearing Its End
So far this year, cloud computing companies are showing steady top-line growth and strengthened fundamentals. This is notable despite persistent headwinds in the first half of the year, including a weakening macro environment, a regional banking crisis weighing down IT budgets, and widespread corporate cost cutting.
Recent earnings reports offered evidence and further boosted investor sentiment. Amazon Web Services’ (AWS) growth stabilize at 12% year-over-year (YoY) in Q2 2023 as customers shifted from cost optimization to deploying new workloads.3 Revenue growth for Microsoft’s Cloud Infrastructure business, Azure, surged by 26% YoY in Q2, beating expectations for 25% growth.4 Google Cloud powered growth at Alphabet by generating $8.03 billion in revenue in Q2 2023, a robust 28% YoY increase.5 Also, the unit achieved profitability on an operating basis for the second quarter in a row.6
Software-as-a-service (SaaS) providers also reported strong growth in Q2, offering more evidence of an improving IT spending environment. Workday, a cloud application company with a focus on human resources, grew its top line by 17% YoY, slightly ahead of consensus expectations. Other companies had similar success: Salesforce grew 11% YoY, ServiceNow by 23% YoY, and Adobe by 10% YoY, all exceeding consensus expectations.7,8,9
While the cloud spending optimization trend will likely persist through the year in some sectors, we expect the cloud computing rebound to continue through the end of the year, enabled by low base effects and stabilized by growing corporate investments in AI.
Hyperscalers and Software Giants Start to Experiment with AI
Large enterprises are looking at AI as a critical tool for productivity gains.10 Solutions aimed at simplifying repetitive processes in customer service, boosting administrative productivity, and improving risk management functions are expected to grow in popularity in the coming days.
Hyperscalers will likely play a central role in transitioning their customers into the AI future, and early indications are that their services are already bringing in revenues. For example, Microsoft’s Azure OpenAI Service added over 6,500 new customers in Q2.11 Microsoft guided for 25–26% YoY growth in the Azure vertical in Q3, with 2 points attributed to AI Services.12
AWS didn’t quantify AI revenues, but management underlined ongoing companywide efforts to identify areas to deliver AI-based solutions to cloud customers. AWS also announced a series of product announcements and partnerships in Q2, including the Amazon Bedrock platform, a service to help customers build and scale generative AI applications, and what could be as much as a $4 billion investment in Anthropic AI, an AI safety and research company.13 Large application vendors such as Salesforce, ServiceNow, Freshdesk, and others are all rolling out a breadth of AI functionalities and features to capture the incremental opportunity with existing customers.14,15,16
The data and information management layer is another area for new launches and partnerships. For example, Mongo dB added vector search functionality to its NoSQL database platform, Atlas, to help make it more conducive to AI development.17 Twilio, in a new partnership with OpenAI, will allow customers to leverage generative AI functionalities inside its customer data platform, Segment. These functionalities can power better tools that generate insights and analysis on customer data.18
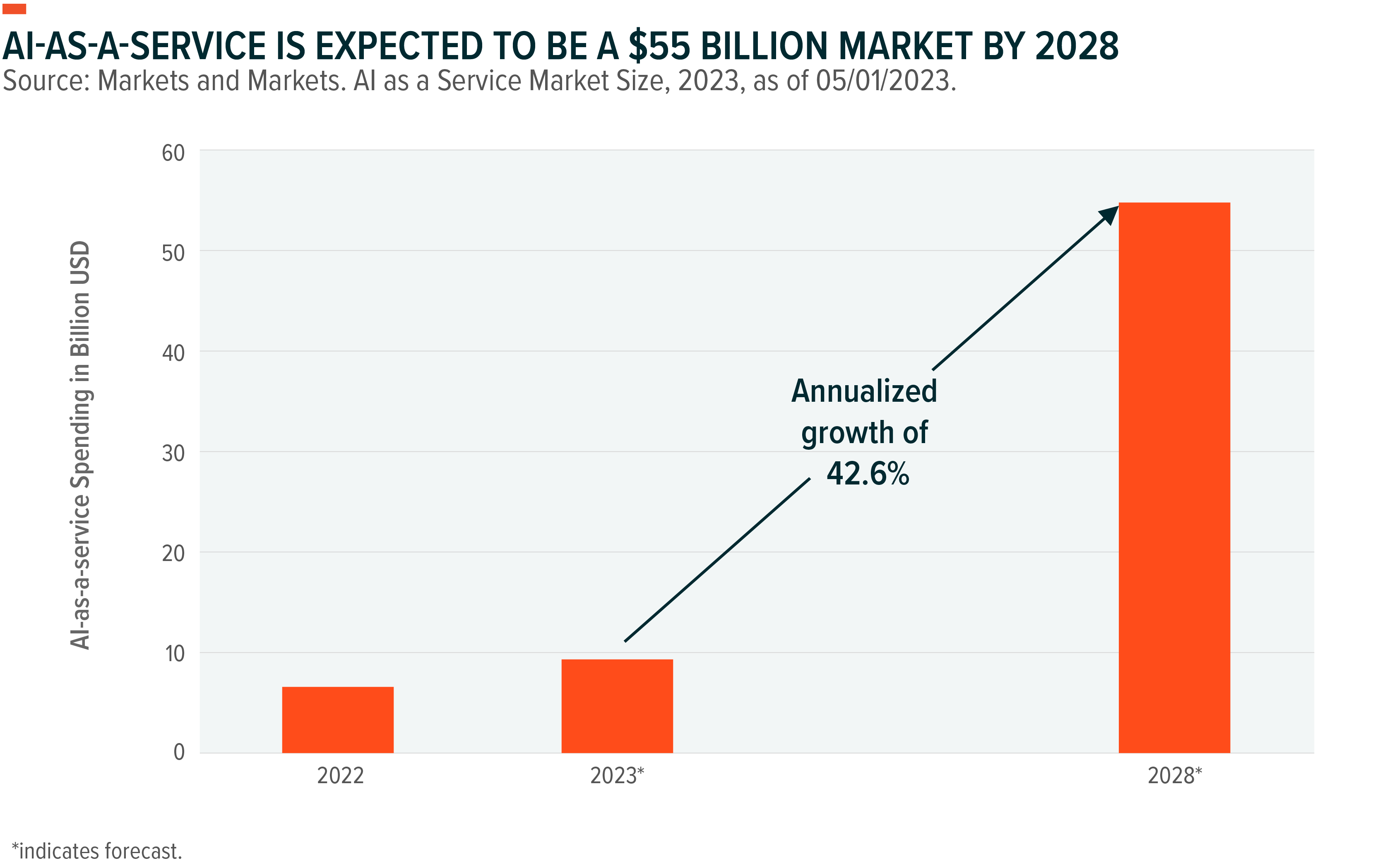
Also, well-funded venture startups are forming relationships with hyperscale vendors, promising cloud computing spending in exchange for access to hyperscalers’ distribution. This cohort could become a major driver of demand in cloud services. Overall, AI-as-a-service, or the business of developing and licensing AI models, is expected to be a $55 billion market by 2028.19
Conclusion: AI Spending Can Drive Cloud Computing Rebound
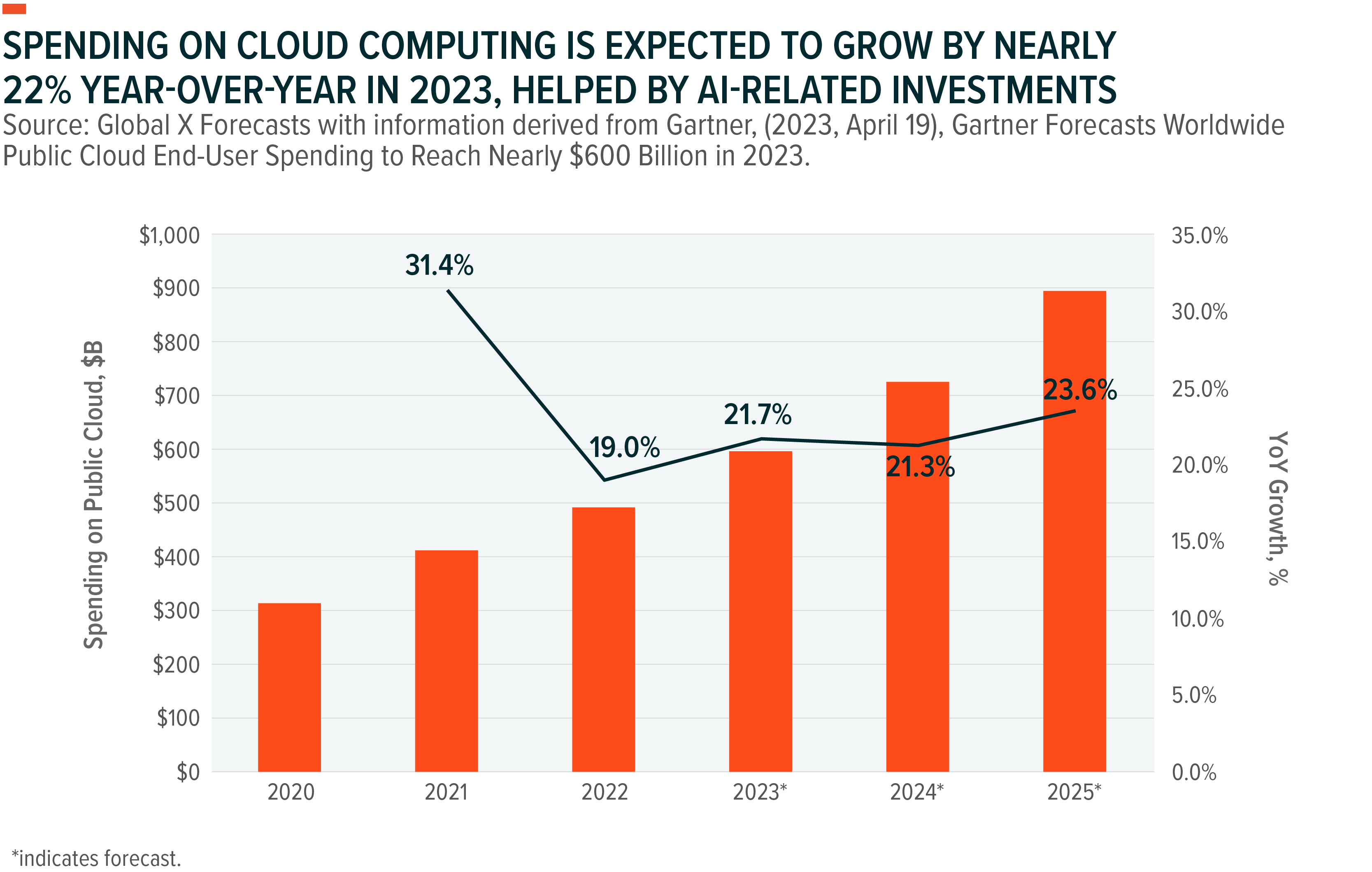
Total global IT spending in 2023 is expected to grow 4.3% YoY to $4.7 trillion marking a swift comeback from 2022.20 Continued investments supporting corporate digital transformations and newly announced AI investments are expected to support further growth. Also, spending on cloud computing is expected to grow 22% YoY to $600 billion for 2023.21 With overall cloud penetration under 20% and AI-related investments accelerating, we believe the Cloud Computing theme’s growth potential is robust.
Related ETFs
AIQ – Artificial Intelligence & Technology ETF
BOTZ – Robotics & Artificial Intelligence ETF
Click the fund name above to view current holdings. Holdings are subject to change. Current and future holdings are subject to risk.
